Tonsillitis/Strep Throat (Recurrent)
Tonsillitis/Strep Throat (Recurrent) – About
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue in the back of the mouth and top of the throat— one tonsil on each side. They help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body. Signs and symptoms of tonsillitis include swollen tonsils, sore throat, difficulty swallowing and tender lymph nodes on the sides of the neck. The tonsils are lymph nodes are thought to assist the body in its defense against incoming bacteria and viruses by helping the body form antibodies. However, this function may only be important during the first year of life. Medical studies have shown that children who have their tonsils and adenoids removed suffer no loss in their future immunity and their ability to fight infections.
Most cases of tonsillitis are caused by infection with a common virus, but bacterial infections also may cause tonsillitis. Tonsillitis is very common in children.
Because appropriate treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause, it’s important to get a prompt and accurate diagnosis. Surgery to remove tonsils, once a common procedure to treat tonsillitis, is usually performed only when bacterial tonsillitis occurs frequently, doesn’t respond to other treatments or causes serious complications.
Strep throat is a contagious disease caused by infection with streptococcal bacteria, which causes inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes lining the back of the throat and the tonsils. It is a common cause of sore throat in school-aged children and teens, and its prompt diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent any potential complications. It is important to note that most cases of sore throat are in fact due to a viral infection (caused by a virus). A viral sore throat typically improves on its own and does not respond to treatment with antibiotics. However, the identification of strep throat is important to prevent the potential complications associated with this illness.
Tonsillitis/Strep Throat (Recurrent) – Diagnosis
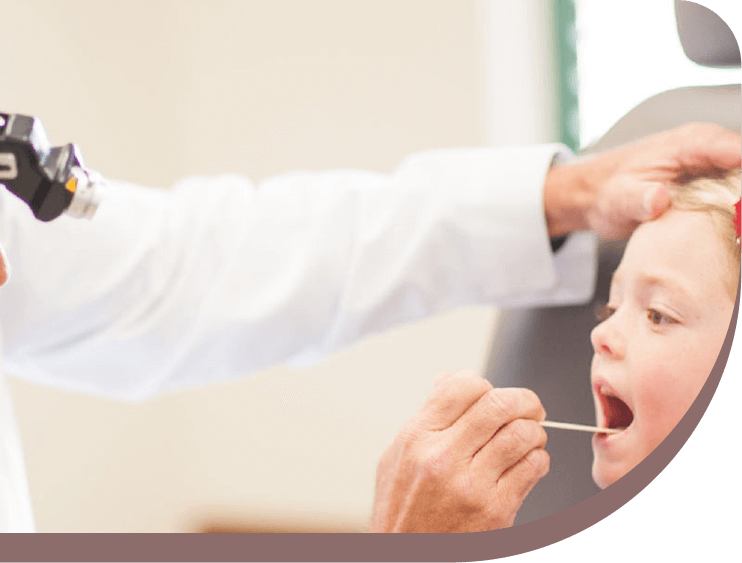
A physical exam from a healthcare provider will include:
- Examination of the throat using a lighted instrument. The ears and nose will alsobe examined as possible sites of infection.
- Checking for rashes (scarlatina) associated with some cases of strep throat
- Examining the neck to check for swollen glands (lymph nodes)
- Checking for enlargement of the spleen (for consideration of mononucleosis, which also inflames the tonsils)
A throat swab – A sterile swab of the back of the throat to get a sample of secretions. The sample will be checked in the doctor’s office or in a lab for streptococcal bacteria. A “rapid strep test” can be done in most doctors’ offices. However, this test may be normal, and you can still have strep. Your doctor may send the throat swab to a laboratory for a strep culture. Test results can take a few days.
Complete blood cell count (CBC) – Your doctor may order a CBC using a small sample of your child’s blood. This test counts the different types of blood cells and can indicate whether an infection is more likely caused by a bacterial or viral agent.. A CBC is not often needed to diagnose strep throat. However, if the strep throat lab test is negative, the CBC may be needed to help determine the cause of tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis/Strep Throat (Recurrent) – Treatment
A mild case of tonsillitis does not necessarily require treatment, especially if a virus, such as a cold, causes it.
Treatments for more severe cases of tonsillitis may include antibiotics or a tonsillectomy.
Surgery to remove the tonsils is called a tonsillectomy. This was once a very common procedure. However, tonsillectomies today are only recommended for people who experience chronic or recurrent tonsillitis. Surgery is also recommend to treat tonsillitis that doesn’t respond to other treatment, or tonsillitis that causes complications.
Conditions Treated
Follow us


Your Health Starts Here
"*" indicates required fields
