Adenoiditis
Adenoiditis – About
Adenoiditis is an inflammation and swelling of the adenoids caused by infection. Adenoids are masses of lymphatic tissue that help the body fight infection. Adenoids are found in the throat, also called the pharynx, just behind the nose. Along with the tonsils, adenoids are the first line of defense against bacteria and viruses. Unlike tonsils, which can be easily seen by opening your mouth, you cannot see the adenoids.
Adenoids are part of the lymphatic system which performs several roles to help protect you from infection. Adenoids store white blood cells and antibodies that help to destroy possible infections threatening your health. If the adenoids become inflamed, they may not perform their function properly and adenoiditis can make breathing difficult and lead to recurring respiratory infections. While adenoids play an important role in keeping a person healthy, as you get older, adenoids become less important, because your body is able to fight infection in other ways. Adenoids often get smaller around age 5 or 6 and virtually disappear by the teen years. For this reason adenoiditis is most commonly seen in children, but can sometimes affect adults.
Adenoiditis – Diagnosis
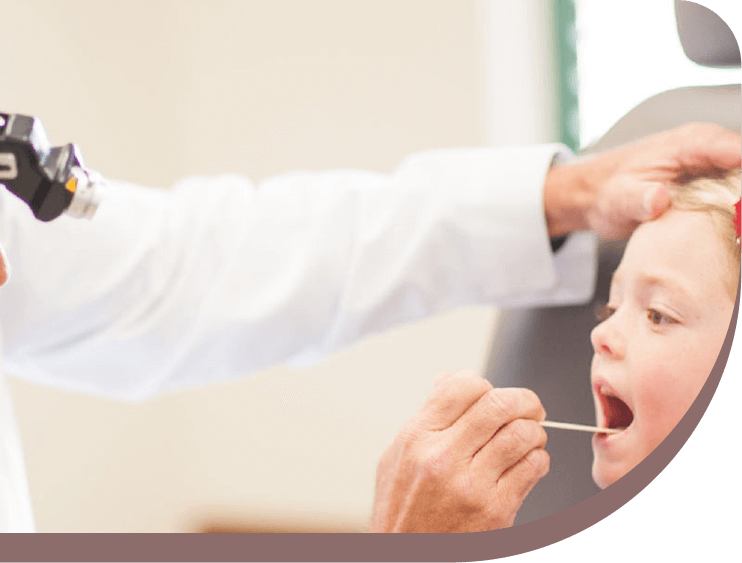
Your doctor may refer you to a specialist called an otolaryngologist. An otolaryngologist is also known as an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor. An ENT doctor has specialized training in infections, diseases, and conditions of the ear, nose, and throat. Your ENT will also ask about your family history to determine if your condition is hereditary and will perform a physical examination to determine where the infection is located. Other tests can include: throat examinations using swabs to obtain samples of bacteria and other organisms; blood tests to determine the presence of organisms; X-rays of your head and neck to determine the size of your adenoids and extent of infection.
Adenoiditis – Treatment
Adenoiditis is treated with antibiotics. If a virus caused your adenoiditis, your doctor will put you on a treatment plan that is specific to the virus. However, if your child has frequent infections, including ear and sinus infections, or antibiotics do not help, or if your child has ongoing breathing problems, surgery may be needed to remove the adenoids. This procedure is called an adenoidectomy.
Your child’s doctor may also recommend the tonsils be removed at the same time since adenoiditis and tonsillitis often go hand in hand. Surgery to remove the tonsils is called a tonsillectomy.
Together, you and your child’s doctor can discuss the pros and cons of surgery and determine if it is necessary.
Conditions Treated
Follow us


Your Health Starts Here
"*" indicates required fields
